PhpStorm, Docker and Xdebug 3 on PHP 8.1 in 2022
In this part of my this tutorial series on developing PHP on Docker we're taking a good hard look at PhpStorm, Xdebug and how to run and debug scripts from within PhpStorm on Docker.
All code samples are publicly available in my Docker PHP Tutorial repository on Github. The branch for this tutorial is part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker.
All published parts of the Docker PHP Tutorial are collected under a dedicated page at Docker PHP Tutorial. The previous part was Setting up PHP, PHP-FPM and NGINX for local development on Docker and the following one is Structuring the Docker setup for PHP Projects.
If you want to follow along, please subscribe to the RSS feed or via email to get automatic notifications when the next part comes out :)
Note: The setup that I am going to use is for demonstration purposes only! I do not recommend that you use it
"as is" as your development setup. Some problems that I won't solve here include:
- everything is owned by root (no dedicated user; that will in particular be problematic for linux users)
- SSH login credentials are hard-coded in the container (inherently insecure)
- host.docker.internal will only exist for Windows and Mac users, NOT for unix users
Table of contents
- Setup: The docker containers
- Run PHP via built-in Docker setup
- Run PHP on Docker via Deployment Configuration
Setup: The docker containers
We will only need the php-cli container for this part.
Luckily, we already have a good understanding on how to create the container, although we'll need to make some
adjustments to make everything work smoothly with PhpStorm. I'm gonna walk you through all the necessary changes,
but I'd still recommend to clone the corresponding git repository docker-php-tutorial
(unless you've already done that in part 1), checkout branch part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker and
build the containers now.
As in part 1, I'm assuming your codebase lives at /c/codesbase:
cd /c/codebase/
git clone https://github.com/paslandau/docker-php-tutorial.git
cd docker-php-tutorial
git checkout part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker
docker-compose build
Further, make sure to open /c/codebase/docker-php-tutorial as a project in PhpStorm.
In general, there are two ways to run PHP from PhpStorm using Docker: 1. via the built-in Docker setup 2. via Deployment Configuration (treating docker more or less like a VM)
Run PHP via built-in Docker setup
This is the "easier" way and should mostly work "out of the box". When you run a PHP script using this method, PhpStorm will start a docker container and configure it automatically (path mappings, network setup, ...). Next, the script in question is executed and the container is stopped afterwards.
Enable docker to communicate on port 2375
Open the Docker Setting in tab "General" and activate the checkbox that says "Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS".
Configure Docker Server in PhpStorm
In PhpStorm, navigate to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Docker. Fill out Name and Engine API URL:
- Name: Docker
- Engine API URL: tcp://localhost:2375
PhpStorm will automatically validate your settings and show a "Connection successful" info below the path mappings box:
Configure Docker PHP CLI Interpreter
Navigate to File | Settings | Languages & Frameworks | PHP. Click on the three dots "..." next to "CLI Interpreter".
In the newly opened pop up click on the "+" sign on the top left and choose "From Docker,Vagrant,VM,Remote..."
Next, choose "Docker" from the radio buttons and select our previously created Docker server (named "Docker").
As image, choose docker-php-tutorial_docker-php-cli:latest (which is one of the images used in this tutorial). If you don't see
this image you've probably not yet built the containers. In that case, please checkout the repo and build the containers:
cd /c/codebase/
git clone https://github.com/paslandau/docker-php-tutorial.git
cd docker-php-tutorial
git checkout part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker
docker-compose build
PhpStorm will now try to create the container and figure out if it can run PHP. If all goes well, you should see the following screenshot with information about the PHP and Xdebug versions in the image/container.
Note: Sometimes, this does not work immediately. If that's the case for you, try to click the "Refresh" icon next to "PHP executable".
After you hit "OK", you'll be back in the PHP Interpreter screen where our newly configured Docker interpreter should be already selected:
Note that PhpStorm has automatically configured the path mappings as -v command line option for the Docker container. After hitting "OK"
one last time, everything is set up.
Run/debug a php script on docker
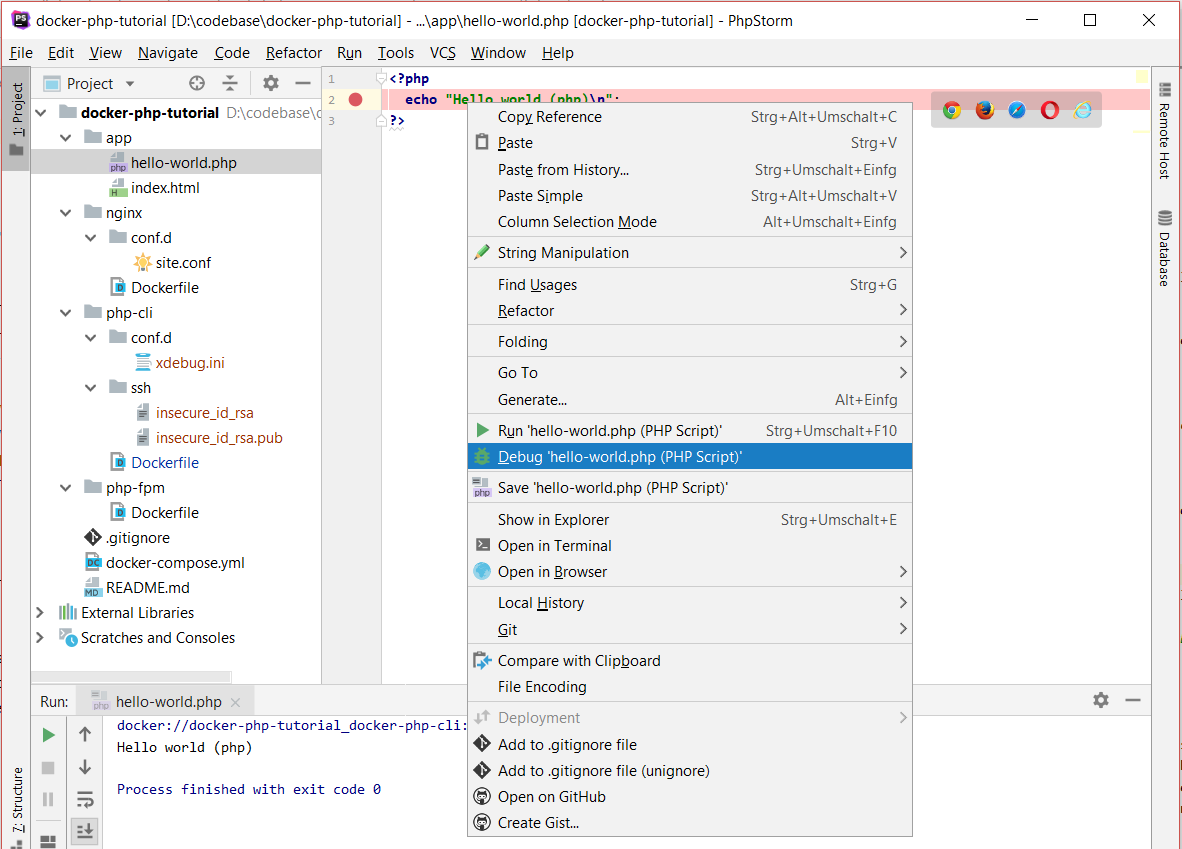
To verify that everything is working, open the file app/hello-world.php in PhpStorm, right click in the editor pane and choose "Run".
PhpStorm will start the configured container and run the script. The output is then visible at the bottom of the IDE:
Since we're using an image that has Xdebug installed, we can also set a breakpoint and use "Debug" instead of "Run" to trigger a debug session:
PhpStorm should stop on the marked line.
When you take a look at the "Console" panel at the bottom of the IDE, you should see something like this:
docker://docker-php-tutorial_docker-php-cli:latest/php -dxdebug.remote_enable=1 -dxdebug.remote_mode=req -dxdebug.remote_port=9000 -dxdebug.remote_host=192.168.10.1 /opt/project/app/hello-world.php
Please keep the -dxdebug.remote_host=192.168.10.1 option in mind - this will be "interesting" when we set up a Docker-based PHP Interpreter
via Deployment Configuration ;)
PS: You find the official documentation for the built-in Docker support at Docker Support in PhpStorm.
Run PHP on Docker via Deployment Configuration
The previously explained method is nice, but it is lacking flexibility and it's also pretty slow as the container used to run the script needs to be started each time we want to execute something. Luckily, there is an additional way of running PHP scripts on Docker in PhpStorm, which is closely related to the Vagrant setup that I explained in Configuring PhpStorm to use the vagrant box.
To make this work, we will keep a docker container running all the time and configure PhpStorm to connect to it via SSH. Thus, PhpStorm effectively treats the docker container as any other remote host.
Preparing the "workspace" container
Please make sure to checkout my demo repository and switch to the correct branch first:
cd /c/codebase/
git clone https://github.com/paslandau/docker-php-tutorial.git
cd docker-php-tutorial
git checkout part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker
For now, we only need the php-cli container. In it, we need to setup the xdebug extension (already done and explained in the previous part) and
an SSH server so that we can log in via SSH. Let's take a look a the Dockerfile:
FROM php:7.0-cli
RUN apt-get update -yqq \
&& apt-get install -yqq \
# install sshd
openssh-server \
# install ping and netcat (for debugging xdebug connectivity)
iputils-ping netcat \
# fix ssh start up bug
# @see https://github.com/ansible/ansible-container/issues/141
&& mkdir /var/run/sshd \
;
# add default public key to authorized_keys
COPY ./ssh/insecure_id_rsa.pub /root/insecure_id_rsa.pub
RUN mkdir -p /root/.ssh \
&& cat /root/insecure_id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys \
&& rm -rf /root/insecure_id_rsa.pub \
;
RUN pecl -q install xdebug-2.6.0 \
;
COPY ./conf.d/xdebug.ini /usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/xdebug.ini
# @see https://docs.docker.com/engine/examples/running_ssh_service/
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"]
and the docker-compose.yml:
docker-php-cli:
# define the directory where the build should happened,
# i.e. where the Dockerfile of the service is located
# all paths are relative to the location of docker-compose.yml
build:
context: ./php-cli
# make the SSH port available via port mapping
ports:
- "2222:22"
# reserve a tty - otherwise the container shuts down immediately
# corresponds to the "-i" flag
tty: true
# mount the app directory of the host to /var/www in the container
# corresponds to the "-v" option
volumes:
- ./app:/var/www
# connect to the network
# corresponds to the "--network" option
networks:
- web-network
There are four things to note:
1. installing the server
2. adding the ssh keys to actually log in
3. changing the default CMD to keep the SSH daemon running
4. port- and volume mapping
Installing the server
The server installation is straight forward:
apt-get install -yqq openssh-server
the only none-intuitive thing is, that we need to "manually" create the directory /var/run/sshd
( due to a bug ).
Adding the ssh keys
For the ssh keys, I'm choosing the easy route (for now) and use a pre-generated ssh key pair (see php-cli/ssh/*).
The content of the public key is appended to /root/.ssh/authorized_keys so that I can log in to the container as user root using the
corresponding private key from php-cli/ssh/insecure_id_rsa.
Caution: Of course, this is massively insecure! Those keys are part of the repository, making them available to everybody with access to the repo. That makes sense for this publicly available tutorial (because everything works "out of the box" for everybody following along) but it is also one of the reasons you should not use that repo as your actual development setup.
Again, there will be another part of this tutorial in which I'll present a solution to this problem (using volumes to share my local ssh keys with a
container and an ENTRYPOINT to put them in the right place).
Keep the SSH daemon running
For SSH to work, we must start sshd and keep it running in the container. We achieve this by using CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"] in the
Dockerfile, following the official docker example to Dockerize an SSH service.
Port- and volume mapping
Since docker containers do not have deterministic IP addresses, we map port 22 from the container to port 2222 on our host machine and we
further provide a path mapping from our local ./app folder to /var/www in the container. Both pieces of information a required when
we configure PhpStorm later on.
Now that everything is in place, let's build and run the container:
cd /c/codebase/docker-php-tutorial
docker-compose up -d docker-php-cli
yielding
Pascal@Landau-Laptop MINGW64 /d/codebase/docker-php-tutorial (part_2_setting-up-phpstorm-with-xdebug-for-local-development-on-docker)
$ docker-compose up -d docker-php-cli
Creating docker-php-tutorial_docker-php-cli_1 ... done
Note: One might argue, that it's kinda defeating the purpose of docker, when we now treat it as a VM, installing SSH and neglecting it's "one process per container" rule. But honestly, I don't care about that when it comes to my local development setup as my main goal is to have something lightweight, that is easily shareable with my team to have a consistent infrastructure setup ;)
Configure the Deployment Configuration
In PhpStorm, navigate to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Deployment.
In the newly opened pop up click on the "+" sign on the top left and choose "From Docker,Vagrant,VM,Remote..." with:
- Name: Docker (SSH)
- Type: SFTP
In the Connection tab, choose the following settings:
- SFTP host: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 2222
- User name: root
- Auth type: Key pair (OpenSSH or PuTTY)
- Private key file: C:\codebase\docker-php-tutorial\php-cli\ssh\insecure_id_rsa
Notes:
- the "Port" corresponds to the port mapping that we defined in the docker-compose.yml file
- the "Private key file" is the "insecure" ssh key that matches the public key we specified in the php-cli/Dockerfile
Hit the "Test SFT connection..." button to test the settings. You should see
(there might also appear a fingerprint warning because we're using 127.0.0.1 as host. You can simply ignore that warning).
Now choose the Mappings tab and fill it the fields as follows:
- Local path: C:\codebase\docker-php-tutorial\app
- Deployment path on server 'Docker (SSH)': /var/www/
Those mappings correspond to the volume definition for the docker-php-cli service in docker-compose.yml:
[...]
# mount the app directory of the host to /var/www in the container
# corresponds to the "-v" option
volumes:
- ./app:/var/www
[...]
Next, we need to create a PHP Interpreter based on our newly created Deployment Configuration.
Open settings and navigate to File | Settings | Languages & Frameworks | PHP. Click on the three dots "..." next to "CLI Interpreter".
In the newly opened pop up click on the "+" sign on the top left and choose "From Docker,Vagrant,VM,Remote..."
Choose "Deployment Configuration" from the radio buttons and select the "Docker (SSH)" entry. Please make sure to enter
/usr/local/bin/php as path for the PHP executable (as PhpStorm by default will set this path to /usr/bin/php).
Set "Docker (SSH)" as name for the new interpreter and click "OK".
Confirm the new PHP Interpreter to close the settings dialog.
Run/debug a php script on docker
To verify that everything is working, open the file app/hello-world.php in PhpStorm, right click in the editor pane and choose "Run".
PhpStorm will start the configured container and run the script. The output is then visible in at the bottom of the IDE:
Since we're using an image that has Xdebug installed, we can also set a breakpoint and use "Debug" instead of "Run" to trigger a debug session:
Hm weird... Although this worked flawlessly when we used the built-in functionality, it does not when we use the Deployment Configuration and shows a "Connection with 'Xdebug 2.6.0' not established." error.
Fix Xdebug on PhpStorm when run from a Docker container
Long story short: There is a bug in the networking setup of Docker for Win that makes PhpStorm use the wrong remote_host when it starts a
debugging session. When you take a look at the "Console" panel at the bottom of the IDE, you should see something like this:
sftp://[email protected]:2222/usr/local/bin/php -dxdebug.remote_enable=1 -dxdebug.remote_mode=req -dxdebug.remote_port=9000 -dxdebug.remote_host=172.18.0.1 /var/www/hello-world.php
The -dxdebug.remote_host=172.18.0.1 option is our suspect here. Luckily, since
Docker v18.03 there is a "magic" DNS entry called `host.docker.internal
that we can use to reach the host from a container.
So, how can we solve this? PhpStorm enables us to
pass custom options to Xdebug when a debugging session is initiated.
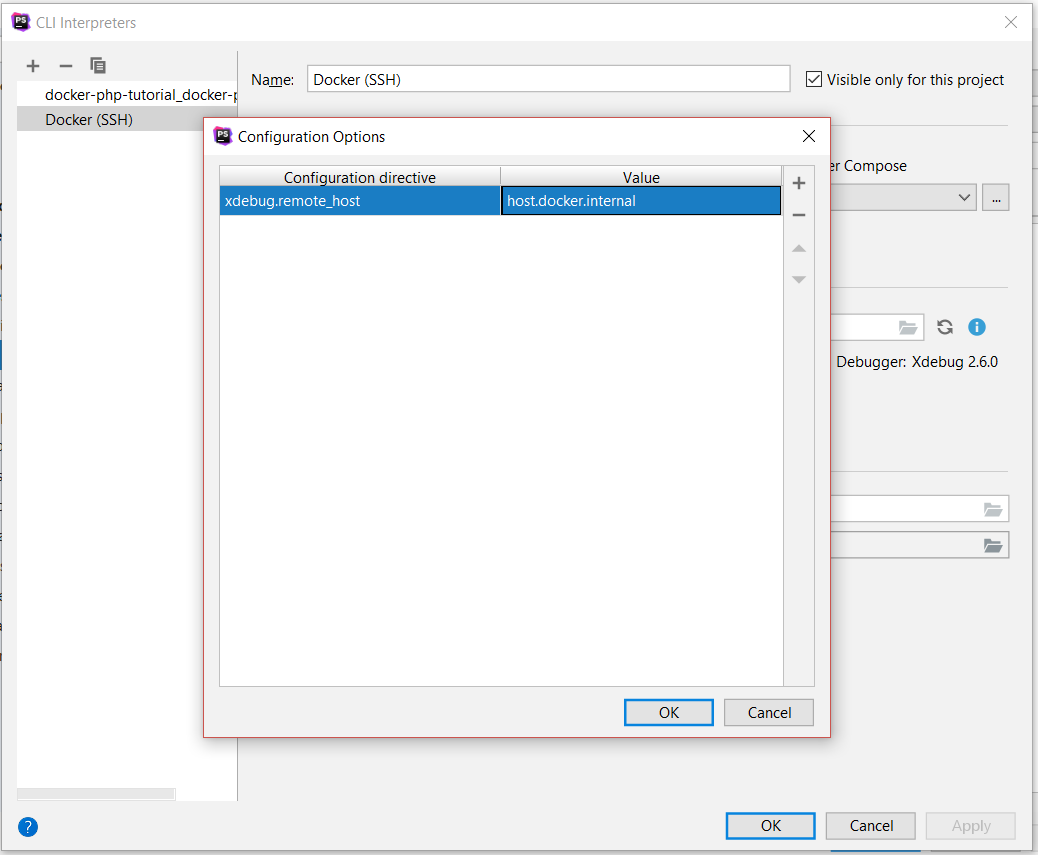
Open File | Settings | Languages & Frameworks | PHP and click on the "..." next to "PHP Interpreter" to bring up the interpreters. Choose
"Docker (SSH)" in the left pane and click on the little folder icon on the bottom of the window next to "Configuration options". In the pop up enter
xdebug.remote_host as key and host.docker.internal as value and hit "OK".
This results in the configuration setting -dxdebug.remote_host=host.docker.internal that is now appended to the remaining (default) arguments
that PhpStorm uses and will override any existing options (including the incorrect xdebug.remote_host).
Initiating a debug session on app/hello-world.php will now finally stop the execution as expected and the
"Console" panel at the bottom of the IDE, shows
sftp://[email protected]:2222/usr/local/bin/php -dxdebug.remote_enable=1 -dxdebug.remote_mode=req -dxdebug.remote_port=9000 -dxdebug.remote_host=172.18.0.1 -dxdebug.remote_host=host.docker.internal /var/www/hello-world.php
This setup denotes the end of the second tutorial. In the next part we will take a much deeper look into Xdebug to fully understand how it works (especially in combination with PhpStorm), how to fix common problems and make it work in different scenarios (debugging from the browser, from php workers, etc.).
Wanna stay in touch?
Since you ended up on this blog, chances are pretty high that you're into Software Development (probably PHP, Laravel, Docker or Google Big Query) and I'm a big fan of feedback and networking.
So - if you'd like to stay in touch, feel free to shoot me an email with a couple of words about yourself and/or connect with me on LinkedIn or Twitter or simply subscribe to my RSS feed or go the crazy route and subscribe via mail and don't forget to leave a comment :)
Subscribe to posts via mail